BIENNIAL CONFERENCE Papers
Theme: Contemporary Approaches to Engineering Education and Practices
Welcome to the SLIE Biennial Conference 2024!We are excited to present a diverse range of paper presentations, all aligned with the six key sub-themes of our conference. Each presentation offers valuable insights and innovative approaches to contemporary engineering challenges. These papers will be presented and explored during the technical sessions outlined in the agenda. Explore the profiles of our presenters and their groundbreaking work below.
Emerging Approaches to Engineering Education and General Practices
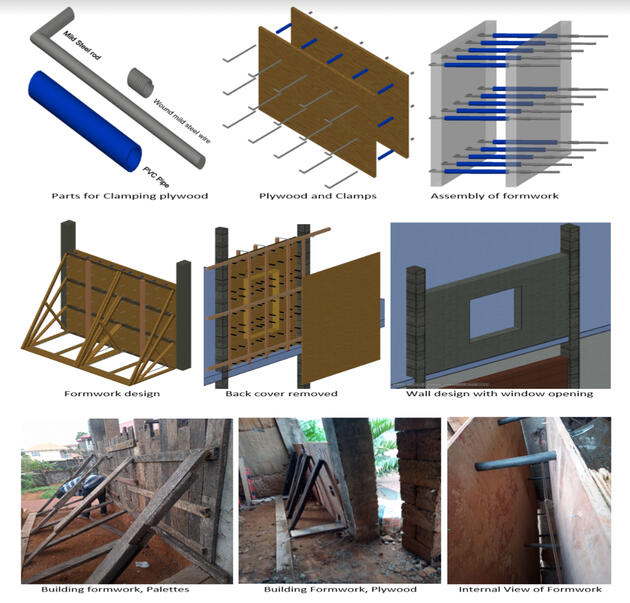
Construction of Walls using a mixture of laterite, cement and mashed paper
Dr Sheriff Kamara, Mechanical and Maintenance Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Fourah Bay College, UoSL
Abstract
The construction industry is currently under enormous change that requires new ways of working and using materials. Accordingly, formwork designs and utilisation of wastes are emerging trends that have been embraced by lots of construction companies to stay competitive. Construction industry in Sierra Leone has to innovate and become more efficient by implementing solutions that are environmentally friendly. The current speed at which buildings are constructed in Sierra Leone, especially in the capital city, Freetown, is unprecedented. Sand and cement are required in huge quantity to satisfy the demand of these construction projects, especially production of building blocks to construct walls. Each block of every course must be plumbed both horizontally and vertically to ensure equal distribution of loads to the floor, which takes time and efforts. Environmental concerns have been raised regarding scarcity of sand in some beaches and rivers in Freetown, that requires urgent solution. A replacement of sand is urgently required. One suitable and cheaper replacement is laterite soil, which consists mainly of sand, clay and gravels, and it binds well with other materials such as paper, ash, sawdust, for example. Cement can be added to laterite to produce strong and durable building blocks. Lighter blocks can be constructed with the addition of mashed paper into the mixture of cement and laterite. In this regard, it is essential to come up with a cheaper and more efficient method of constructing walls, using wastes. Accordingly, this study was undertaken to help solve this problem. A formwork with the same dimensions of the wall to be constructed was built and filled with a mixture of laterite, mashed paper and cement and allowed to solidify. The recommended percentage of cement in sandcrete block is 15%, while that for mortar bedding is 25%. Therefore, percentage of cement in the laterite-cement mixture was obtained by taking the average of the two percentages. Cubes were cast from this mixture, cured and tested in the lab for compressive strength. Calculations for water absorption and bulk density were also carried out. The results show compressive strength, Bulk density and Water absorption rate of 6.2 N/mm 2 , 1700 kg/m 3 , and 15% respectively. These values are above the recommended values stipulated by BS2028 and ASTMC90 for load bearing walls. Therefore, this study finds out that laterite-cement with mashed paper as admixture can be used to construct walls that are cheaper with the required quality.The graphical abstract presented hereunder is meant to increase comprehension of the concepts used to design and construct the wall.Technical Session: 3

Factors affecting sustainable solar power output
Ing Brian Conton, Sierra Leone Institution of Engineers
Abstract
Solar power is seen as an extremely viable power alternative in the tropics. In Sierra leone, most people are surprised by the variations in performances of systems once installed. These variations don’t just exist across different systems but also intra systems across different periods of the year. No shocks during the rainy season when it can dark and overcast. This is the period of quantitative shortage. However during the dry season there are somewhat “unexplainable” periods of low power which tend to be more qualitative in nature. This paper helps analyse how even in the quantitative abundance of sunlight during the dry season the quality of the light can cause power shortfalls.Technical Session: 3
SENSEBOD - Artificial Intelligence in Education
Ing Abdul Rahman Jalloh, Sierra Leone Institution of Engineers
Abstract
Artificial Intelligence (AI) holds significant potential to transform education, as evidenced by its implementation in prestigious institutions like Harvard and EdTech companies such as Khan Academy. In Sierra Leone, the education system faces numerous challenges, including a shortage of qualified teachers, limited access to contemporary knowledge, and difficulties in explaining complex concepts, particularly to students in remote areas with limited English proficiency.To address these issues, we introduce Sensebod, an all-in-one educational platform designed to enhance learning outcomes. Central to Sensebod is 'Tichalemplemp,' an AI teacher that facilitates personalized learning by simplifying complex subject material. Our user requirement gathering research, which involved a sample of students from 15 schools in Freetown, was conducted over a period of four months and included both qualitative and quantitative data collection methods. The results indicated that 58% of secondary school students already use AI tools for educational purposes, highlighting the need for a more tailored educational tool. Sensebod uniquely supports local languages through its English-to-local language converter, addressing the 48% of students who struggle with English and the 82% who prefer learning in their native languages.Sensebod also emphasizes mentorship by integrating both human and AI-driven mentors, creating online communities for collaborative learning, and fostering research and support. This feature is crucial for the 75% of surveyed students who emphasizes the need for mentorship. Additionally, Sensebod provides early intervention by identifying students at risk of underachievement.
Significantly, Sensebod extends its reach beyond the 29% of Sierra Leoneans with internet access by offering offline functionalities via the Easy STEM server, ensuring inclusivity and accessibility even in remote villages. Our commitment to open data and innovation allows stakeholders and researchers to access insights into students' learning patterns, promoting data-driven decision-making to improve educational outcomes.Technical Session: 3
A Two-Stage Bootstrap-DEA and Ordinary Least Square Approach for Efficiency-Based Assessment of Paratransit Services in Mixed Traffic
Ing Simeon Stevenson Turay, Charles Anum Adams, Augustus Ababio-Donkor; Regional Transport Research and Education Centre Kumasi (TRECK), Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana 1Ph.D. Research Scholar, Regional Transport Research and Education Centre Kumasi (TRECK), Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana
Abstract
There has been a surge in the use of paratransit including minibus, two and three-wheelers, and other variants in Sub-Saharan African cities. Despite being characterized as unsafe; they continue to address a greater percentage of urban travel demand. Amidst the ongoing debate to integrate public bus and paratransit services, there is a need to understand the current performance of the existing modes operating in mixed traffic. The present study attempts to evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness measures of paratransit services using two- stage data envelopment analysis (DEA). In the first stage, efficiency and effectiveness scores for paratransit services along two corridors were evaluated. In the second stage, conventional DEA efficiency scores were corrected for bias by bootstrapping and regressed against a set of operational indicators. Data collection included videography, onboard vehicle, user perception, and operator surveys. A total of 1,119 drivers and 1,010 passengers were intercepted, and 300 onboard trips were made. Data were analyzed in STATA and deaR software programs. Findings revealed that as compared to low-capacity modes, relatively high-capacity modes are more efficient and effective in terms of revenue-generating vehicle kilometers traveled and daily ridership. Efficiency was found to be positively influenced by passenger density, speed density, and vehicle capacity. Stop density, overloading, in-vehicle travel time, trip delay and fuel consumption had a significant negative impact on paratransit services. These findings provide an opportunity to develop more precise planning strategies to increase the performance of paratransit services especially for cities moving towards integrating informal public transport into the mainstream transit planning and policy processes.Technical Session: 3
Understanding Commercial Bike Riders (Okada) and Three Wheel Commercial Vehicle Riders (Kekeh) Operations in Sierra Leone
Ing Georgette Green - MSLIE, Sierra Leone Institution of Engineers
Abstract
High levels of road congestion impact urban productivity as economically productive hours are wasted in traffic getting from point A to point B.
Congestion is one of the major challenges to urban mobility in Freetown. A major contributing factor to this challenge is the operation of two and three wheelers (okadas and kekehs) who usually ignore traffic rules, congregate disorderly at intersections and are one of the leading causes of road traffic incidents and accidents according to the Sierra Leone Police Road Accident Data for 2019.During the implementation of the Integrated and Resilient Urban Mobility Project (IRUMP), it became apparent that initiatives to manage traffic and increase traffic law compliance would be necessary for the sustainability of the project.Following development of the traffic management plan through a multi-agency coordinated approach, the project team tried to understand the okada and kekeh operations in a bid to provide support for a modernization and professionalization process. This decision was taken to enable operators improve their level and quality of service and thereby support last mile connectivity of the IRUMP corridor, thereby ensuring the sustainability of the Integrated and Resilient Urban Mobility Project and as a result embedding project outcomes into the statutory institutions.In addition to the accidents and road safety issues, the rising number of okadas and kekehs (low occupancy vehicles) contribute to the noise and air pollution in the city which in turn contribute to public health issues.On the other hand, okadas and kekes provide a valuable public transport service which large buses cannot be eliminated, at least not in the short term.Along the west IRUMP corridor, the team identified 3 intersections where the operations of the Okadas and Kekes are major contributors to congestion, which are Lumley, Aberdeen and Murray Town intersections.A total of 100 okada and 54 kekeh riders volunteered to complete this survey which including safety considerations such as PPE compliance and adherence to traffic rules alongside demographics such as gender and age.It can be concluded, that okada and kekeh operations are a largely unregulated and unsafe mode of transportation; a very youthful male-dominated industry with less than 1% female riders. These young men may not prioritize their safety due to their need for earning a living as well as creating employment especially when they cannot carry on formal education.A key recommendation is regulating this mode of transportation through the implementation of zonal licensing and capacity building.Technical Session: 3
AI in Education and General Practices
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Digital Tools for Engineering Practices
Engr. Dr. Mudasiru Bola J., FNSE,Nigerian Society of Engineers (NSE)
Abstract
The World Economic Forum has estimated that artificial intelligence will replace some 85 million jobs
by 2025. Freethink says that 65% of retail jobs could be automated by that year, saying that this is
largely due to technological advancements, rising costs and wages, tight labor markets, and reduced
consumer spending. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is expected to have a significant impact on the job
market. According to a report from the World Economic Forum, around 40% of all working hours
could be impacted by AI, particularly large language models like ChatGPT-4. Jobs in clerical or
secretarial roles are likely to decline quickly due to AI, while roles for AI and machine learning
specialists, data analysts and scientists, and digital transformation specialists are expected to grow
rapidly. The adoption of AI is anticipated to lead to job growth in sectors such as health (22%),
scientific and technical services (16%), and education (6%). On the other hand, some sectors might see
a decline in job availability due to AI, including manufacturing jobs by 25%, transport and storage jobs
by 22%, and public administration jobs by 18%. It is important to note that while AI may replace
certain tasks, it also creates opportunities for new roles and industries, emphasizing the need for
reskilling and adapting to the evolving job landscape.Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, ChatGPT-4, digital tools, job landscape, technological advancementsTechnical Session: 1
AI in Education and General Practices: Enhancing Learning and Operational Efficiency
Napoleon T. Chattah, MIDA, BSc, A.M.ASCE, CEO/Project Manager, Liberia Engineering and Trade Corporation (LETCO) | CEO/Co-Founder, Tyneceploh Educational Foundation
Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionising education and general practices by enhancing learning experiences and operational efficiency. In education, AI facilitates personalised learning, intelligent tutoring systems, smart content creation, automated grading, and predictive analytics for student success. These applications improve engagement, performance, and administrative processes. In healthcare, AI optimises treatment plans, predicts diseases, standardises therapy, and streamlines medical research and drug development. In engineering, AI enhances design processes, predicts system failures, standardises procedures, and accelerates research and development. Ethical considerations and data safety guidelines are crucial for responsible AI implementation across these fields. Overall, AI's role in education and general practices is pivotal in advancing learning, efficiency, engineering innovations, and patient care.Technical Session: 2
AI and Workforce Transformation in the Engineering Sector: Evolving Job Roles, Skills Requirements, and Future Predictions
Ing. Obinna Anthony Browne - MSLIE, Sierra Leone Institution of Engineers
Abstract
The advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is profoundly transforming various
industries, including the engineering sector. AI is revolutionizing industries by automating tasks,
enhancing efficiency, and enabling new capabilities. The engineering sector, characterized by its
reliance on precision, innovation, and complex problem-solving, is undergoing significant
changes due to AI. This paper explores how AI is reshaping job roles and skills requirements for
engineers, providing insights into the present changes and future implications. It delves into the
transformative impact on engineering education and practice, predicting how AI will continue to
influence the profession.Technical Session: 4
Continuous Professional Development or Lifelong Learning
Continuous Professional Development - Fostering a Culture of Adaptive and Lifelong Learning for Engineers
Ing. Festus Oba Agwu-Jones, PE FSLIE, President Elect, Sierra Leone Institution of Engineers
Abstract
This presentation highlights the significance of encouraging the development of soft skills and leadership skills as a requirement for Lifelong learning for engineers.Why do engineers need additional skills? We live in an ever-changing world, and if you are not always learning, you will be left behind.Hard skills or technical skills are learned through education or hands on experience, but to become a well-rounded engineer, these hard skills need to be complimented with soft skills. Soft skills are personal attributes that influence how well we can work or interact with others. They make it easier to form relationships with people, create trust and dependability and lead teams. We need these additional skills and knowledge to helps us identify technical problems and create solutions in an ever changing and demanding environment. Being a well-rounded engineer can be important for one’s professional success in the future. It allows one to excel at their current responsibilities and take on new tasks outside of their role. This can help diversify their daily routine and allow for opportunities to work on new assignments and projects. A well-rounded engineer is then able to handle a variety of situations and problems without requiring assistance. Importantly, being well-rounded can allow an engineer to explore a variety of job titles.With the identified risk of AI taking over jobs, which is underpinned by FOMO (Fear of missing out) – being left behind due to not having the skills to render one capable to meet the demands of AI driven jobs in addition to the worry that this new technology will completely eliminate their current roles. This presentation identifies the high-income skills that AI can’t replace.The presentation concludes on the skills necessary for the future of leadership. Not only has the world changed, so has the nature of work itself, along with the workplace and the workforce, inclusion, collaboration and innovation are no longer simply buzzwords but are the price of entry to being successful in our current as well as every future reality. The future of leadership is changing from Command & Control to Trust & Inspire.
Technical Session: 1
Addressing Climate Vulnerability
Towards Net Zero Internet of Things (IoT) System - MSc. Project
Ing. Davephine Tholley - MSLIE, Sierra Leone Institution of Engineers
Abstract
As climate change continues to ravage the world, it is crucial to have a real-time flood monitoring
Internet of Things system. This system has the advantage of contributing to Net Zero, providing
real-time data, and mitigating damages caused by flooding.This paper, undertaken as part of the author’s MSc. in Engineering Business Management degree at
the University of Sussex, presents the design and development of a prototype flood-monitoring
Internet of Things (IoT) system.Following a literature review of existing papers on different prototypes, the design of a flood
monitoring IoT system was built considering its use case in Sierra Leone, considering cost and
geography. The prototype design includes two Arduino ESP32 microcontrollers, two LoRa modules
for data transmission, an ultrasonic sensor, a humidity and temperature sensor, a rain density sensor,
and a soil moisture sensor. The use of mini solar modules to test the use case of clean energy with IoT
as an energy-efficient solution is vital towards Net Zero. The codes of this prototype were sourced and
edited. The results prove that the system works. There was limited testing, so more data is needed to
evaluate the accuracy and efficiency.Keywords: Flood monitoring, Internet of Things systemTechnical Session: 4
Engineering Diplomacy: A Useful Tool in Foreign Diplomacy
Engineering Diplomacy: A Useful Tool in Foreign Policy
Ing. Tatiana Sesay, CEO of MOG Investment, Sierra Leone
Abstract
The fundamental role of engineering in modern science diplomacy should not be
overlooked. The intended objectives of engineering for diplomacy with other
nations—developed and developing—can be as varied as supporting education and research
capacity, exchanging faculty and students, and “building bridges” via partnerships to
implement engineering and technology-related projects. Such activities have increasingly
characterized recent programs by some developed nations in the world.Modern engineering projects, highly interdisciplinary and using a multifaceted thinking
process, can greatly contribute to economic progress and the bridging of differences between
countries. Engineering can be characterized by two main features: a systems orientation and
“design under constraints.”“Engineering is about systems - Engineering activities are already well integrated into many
formal, government-to-government agreements and memoranda for cooperation between the
United States and other countries, China and countries in Africa, the United Kingdom and
other Developing Countries, etc. Outside the government, many laboratories, universities,
and private sector companies have even more extensive science and engineering relationships
that complement official diplomacy.Keywords: engineering diplomacy, foreign policy, global stability, engineering expertise, transnational challenges, sustainable development, infrastructure diplomacy, technological innovation, cross-cultural communicationTechnical Session: 1
Gender Perspective in Engineering Education
Ing Trudy Morgan - FSLIE, President, Sierra Leone Institution of Engineers
Abstract
Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) are vital to the economic and social prosperity of countries. Sierra Leone is a developing country and relies on every sector to effectively contribute to its growth and development. Engineering contributes to economic growth by developing infrastructure, creating new technologies and improving productivity in various sectors. Engineers work to solve problems in all sectors including infrastructure, health, transportation and even education.In 2023, men outnumbered women in the global engineering workforce 86.3% to 13.7%. While this percentage of women in engineering is a decrease from 14.88% in 2020, figures over the years indicate a general increase in the percentage of women employed in engineering worldwide. Sierra Leone labour force participation rate for 2022 was 31.20%, a 0.07% decline from 2021. The female labour force of Sierra Leone fell gradually from 50.7 % in 2004 to 47.92 % in 2023. The Sierra Leone Institution of Engineers (SLIE) has as its strategic objective to increase the participation of girls and women in engineering as women and girls continue to be underrepresented in STEM related activities and careers.Through collaboration with Imperial College London, and with funding from the Royal Academy of Engineering, SLIE undertook a pilot research study to explore female participation in engineering in Sierra Leone. This presentation looks at some of the systemic barriers that could represent an impediment for female students’ participation in engineering programs; explores some of the challenges experienced by professional female engineers; and highlights work being undertaken to increase female participation in engineering by the Sierra Leone Institution of Engineers.Technical Session: 4